Peer review is a cornerstone of academic, scientific, and professional excellence. This systematic process ensures that work submitted for publication or evaluation meets high-quality standards by undergoing scrutiny from experts in the same field. From research papers to project proposals, peer review plays a pivotal role in validating the authenticity, relevance, and accuracy of information. Its importance cannot be overstated, as it fosters trust and credibility while advancing knowledge.
Beyond its role in academia, peer review is increasingly used across industries, including healthcare, engineering, and technology, to maintain and improve quality assurance. By eliminating errors, detecting inconsistencies, and providing constructive feedback, peer review nurtures continuous improvement. Whether you're a researcher, a student, or a professional, understanding how peer review works can empower you to contribute more effectively to your field.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve deep into the intricacies of peer review, exploring its origins, types, processes, and significance. We’ll also tackle common challenges, ethical considerations, and best practices for conducting and receiving peer reviews. By the end of this article, you’ll have a thorough understanding of peer review and its far-reaching impact on enhancing quality and credibility.
Read also:Racheal Lot A Multifaceted Persona In Todays World
Table of Contents
- What is Peer Review?
- History and Evolution of Peer Review
- How Does Peer Review Work?
- Types of Peer Review
- Importance of Peer Review in Academia and Beyond
- What Are the Common Challenges in Peer Review?
- How to Conduct an Effective Peer Review?
- Ethical Considerations in Peer Review
- Benefits of Peer Review for Authors and Reviewers
- Impact of Peer Review on Scientific Advancement
- Peer Review vs. Editorial Review: What’s the Difference?
- How Can You Receive Constructive Feedback from Peer Review?
- Future Trends in Peer Review
- Frequently Asked Questions About Peer Review
- Conclusion
What is Peer Review?
Peer review is a structured process where experts in a given field evaluate the work of their peers to ensure its quality, validity, and relevance. This evaluation can apply to research papers, grant proposals, or even product designs. The core principle of peer review is impartiality, as reviewers judge the work based on its merit rather than personal biases.
Peer review acts as a filter, ensuring that only high-quality work gets published or approved. It also serves as a collaborative process, allowing authors to refine their work based on constructive feedback. This mechanism not only enhances the credibility of the work but also drives innovation by encouraging rigorous scrutiny and dialogue among experts.
History and Evolution of Peer Review
The concept of peer review dates back to ancient times when scholars would seek feedback from their contemporaries to validate their work. However, the modern peer review system began to take shape in the 17th century with the establishment of scientific journals like the "Philosophical Transactions" of the Royal Society.
Over the centuries, peer review has evolved into a more formalized and systematic process. Today, it is considered the gold standard for maintaining the integrity and reliability of academic and professional work. Technological advancements have further revolutionized peer review, introducing digital platforms that streamline the submission and evaluation process.
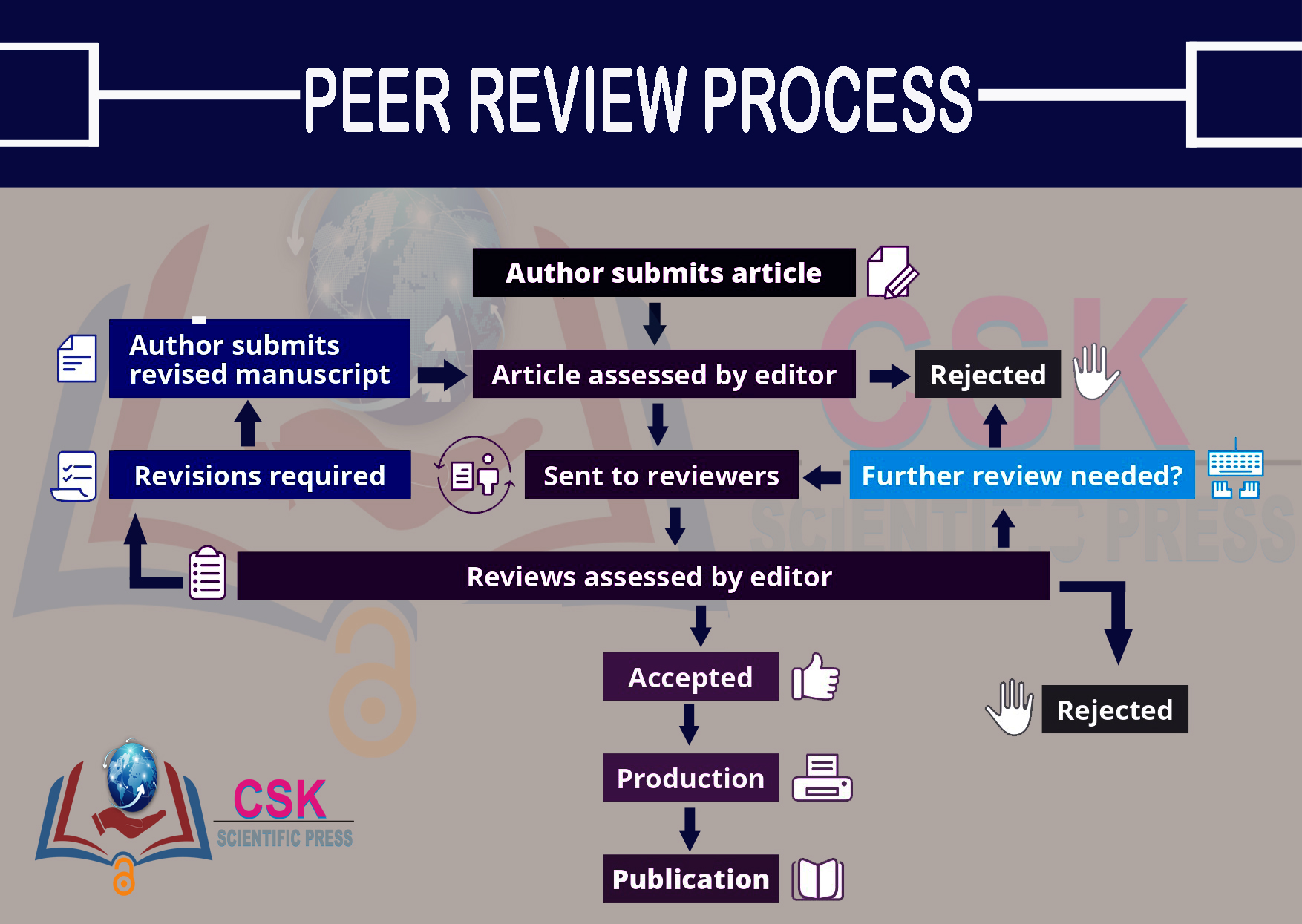
How Does Peer Review Work?
The peer review process typically involves several steps:
- Submission: Authors submit their work to a journal, conference, or organization.
- Initial Screening: Editors perform a preliminary review to ensure the work meets basic criteria.
- Assignment to Reviewers: Experts in the field are invited to evaluate the work.
- Evaluation: Reviewers assess the work for originality, accuracy, and relevance.
- Feedback: Reviewers provide constructive comments and recommendations.
- Decision: Based on the reviewers' feedback, the editor makes the final decision to accept, revise, or reject the work.
Each step is crucial for ensuring the integrity and quality of the peer review process. Transparency and ethical guidelines play a significant role in maintaining its credibility.
Read also:Secrets Of Success In Arena Breakout Infinite Tips Amp Strategies
Types of Peer Review
Peer review is not a one-size-fits-all process. Different types of peer review are suited for different purposes and contexts. Below are the three most common types:
Single-Blind Peer Review
In this type, reviewers know the identity of the authors, but the authors remain unaware of the reviewers' identities. This anonymity allows reviewers to provide honest feedback without fear of backlash.
Double-Blind Peer Review
Here, both the authors and reviewers remain anonymous to each other. This approach aims to eliminate bias and ensure a fair evaluation process.
Open Peer Review
Open peer review promotes transparency by revealing the identities of both authors and reviewers. This type fosters accountability and encourages constructive dialogue.
Importance of Peer Review in Academia and Beyond
The significance of peer review extends far beyond academia. It serves as a quality control mechanism that upholds the integrity of published work. In addition:
- It ensures the accuracy and validity of research findings.
- It provides constructive feedback to authors, helping them improve their work.
- It fosters collaboration and knowledge sharing among experts.
What Are the Common Challenges in Peer Review?
Despite its importance, the peer review process is not without challenges. These include:
- Bias: Reviewers may have unconscious biases that affect their judgment.
- Time Constraints: The review process can be time-consuming, delaying publication.
- Lack of Transparency: Some types of peer review lack transparency, which can lead to mistrust.
How to Conduct an Effective Peer Review?
Conducting an effective peer review requires a structured approach:
- Understand the Guidelines: Familiarize yourself with the review criteria and expectations.
- Be Objective: Focus on the work, not the author.
- Provide Constructive Feedback: Highlight strengths and offer actionable suggestions for improvement.
- Maintain Confidentiality: Respect the confidentiality of the review process.
Ethical Considerations in Peer Review
Ethical guidelines are the backbone of the peer review process. They include:
- Avoiding conflicts of interest.
- Ensuring confidentiality.
- Providing unbiased and honest feedback.
Benefits of Peer Review for Authors and Reviewers
Peer review offers numerous benefits:
- For Authors: It helps improve the quality and credibility of their work.
- For Reviewers: It provides an opportunity to contribute to their field and stay updated on the latest research.
Impact of Peer Review on Scientific Advancement
Peer review has a profound impact on scientific progress. By ensuring the accuracy and reliability of published research, it lays the foundation for future discoveries and innovations.
Peer Review vs. Editorial Review: What’s the Difference?
While both processes aim to ensure quality, they differ in scope and focus. Peer review involves subject-matter experts, whereas editorial review focuses on grammar, style, and formatting.
How Can You Receive Constructive Feedback from Peer Review?
Receiving feedback can be daunting, but it’s an essential part of growth. Here’s how you can make the most of it:
- Keep an open mind.
- Focus on the feedback, not the tone.
- Use the suggestions to improve your work.
Future Trends in Peer Review
The future of peer review is likely to be shaped by technology. Innovations like artificial intelligence and blockchain have the potential to make the process more efficient and transparent.
Frequently Asked Questions About Peer Review
- What is the main purpose of peer review? The main purpose is to ensure the quality, validity, and reliability of scholarly work.
- How long does the peer review process take? It varies but typically ranges from a few weeks to several months.
- Can authors suggest reviewers? Yes, many journals allow authors to suggest potential reviewers.
- Is peer review mandatory for all publications? No, but it is highly recommended for academic and scientific works.
- What happens if a paper is rejected? Authors can revise and resubmit or submit to another journal.
- How is bias minimized in peer review? Double-blind peer review is one method used to minimize bias.
Conclusion
Peer review is an indispensable tool for maintaining the integrity and quality of academic, scientific, and professional work. By understanding its intricacies and adhering to ethical guidelines, we can ensure that it continues to serve as a cornerstone of advancement and innovation.
Article Recommendations