When it comes to amphibians, the terms "frog" and "toad" are often used interchangeably. However, these two fascinating creatures are far from identical. Their physical characteristics, habitats, behavior, and even reproductive strategies showcase distinct differences. While they share a common ancestry and belong to the order Anura, frogs and toads have adapted to their environments in unique ways over millions of years. Understanding these differences can help us appreciate the beauty and diversity of the natural world.
Whether you're a curious student, a nature enthusiast, or simply someone who wants to settle a long-standing debate, this article will break down the key distinctions between frogs and toads. From their physical appearance to their habitats and lifecycles, we’ll delve into every detail that sets them apart. By the end, you'll have a clear answer to the question: What makes a frog different from a toad?
Let’s dive deeper into the fascinating world of these amphibians, exploring their biology, behavior, and ecological importance. Along the way, we’ll also address some common myths and questions about frog vs toad, ensuring this guide is your ultimate resource for understanding these captivating creatures.
Read also:Exceptional Life Of John Taylor From Duran Duran A Rock Icon
Table of Contents
- Physical Characteristics: How Do Frogs and Toads Look Different?
- Habitat and Distribution: Where Do Frogs and Toads Live?
- Skin and Texture: What Sets Frogs and Toads Apart?
- Behavior and Lifestyle: How Do Frogs and Toads Behave?
- Reproduction and Lifecycle: How Do Frogs and Toads Reproduce?
- Dietary Habits: What Do Frogs and Toads Eat?
- Predators and Defense: How Do Frogs and Toads Protect Themselves?
- Frog vs Toad Evolution: How Are They Related?
- Ecological Role: Why Are Frogs and Toads Important?
- Common Myths: Are Frogs and Toads Really That Different?
- Can You Tell Them Apart at a Glance?
- Frog vs Toad in Popular Culture
- How to Care for Frogs and Toads as Pets?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
Physical Characteristics: How Do Frogs and Toads Look Different?
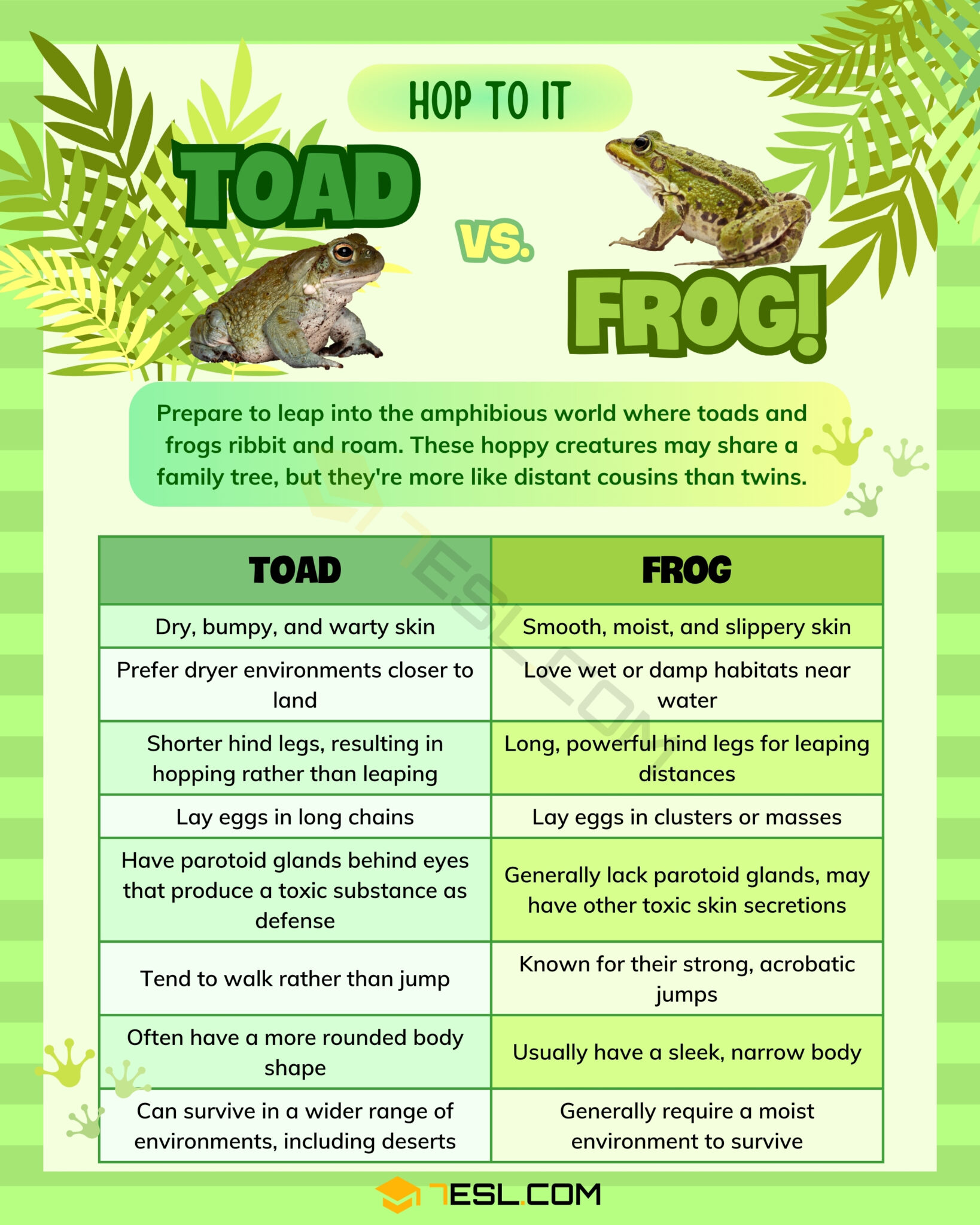
Frogs and toads are both amphibians, but their appearances are so distinct that even a casual observer can differentiate between the two. Frogs are known for their smooth, moist skin, long legs, and slender bodies. They are typically built for jumping and swimming, which is why their hind legs are so powerful. On the other hand, toads have dry, warty skin, shorter legs, and a stockier build, making them more suited for walking or short hops than long leaps.
Frogs often have bright, vivid colors, especially species that are toxic to predators. These colors serve as a warning sign, also known as aposematism. Toads, however, are usually brown, gray, or olive in color, blending seamlessly into their surroundings. Their camouflaged appearance helps them avoid predators in terrestrial habitats.
- Eyes: Frogs have bulging eyes that sit on the top of their heads, giving them excellent peripheral vision. Toads' eyes are less prominent and often appear more recessed.
- Feet: Frogs have webbed feet for swimming, while toads have more separated toes suited for walking on land.
- Size: Frogs are generally smaller and more lightweight compared to the robust and heavier toads.
In summary, the physical characteristics of frogs and toads are shaped by their environments and lifestyles. These traits are not just aesthetic but functional, playing a crucial role in their survival.
Habitat and Distribution: Where Do Frogs and Toads Live?
One of the most significant differences between frogs and toads lies in their choice of habitat. Frogs are closely associated with water bodies such as ponds, lakes, and streams. Their moist skin requires them to stay in or near water to prevent dehydration. Toads, on the other hand, are more terrestrial and can often be found in drier environments like forests, grasslands, and even deserts.
Frogs are widespread across tropical and subtropical regions, thriving in humid climates. Toads, being more adaptable, are found in a broader range of habitats, including arid and semi-arid areas. Their ability to retain moisture and their specialized burrowing behavior allow them to survive in less favorable conditions.
Interestingly, some species of frogs and toads defy these generalizations. For example, the desert rain frog (a type of frog) is adapted to arid conditions, while some toad species prefer moist environments. These exceptions highlight the incredible adaptability of amphibians.
Read also:Mckamey Manor A Deep Dive Into The Haunting Experience
Skin and Texture: What Sets Frogs and Toads Apart?
The texture of their skin is another key difference between frogs and toads. Frogs have smooth, slimy skin that helps them breathe through their skin, a process known as cutaneous respiration. This trait is vital for their aquatic lifestyle.
Toads, however, have rough, bumpy skin due to the presence of glandular warts. These warts are not harmful to humans but play a role in secreting toxins that deter predators. The rough texture also helps them retain moisture, allowing them to venture further away from water sources.
Behavior and Lifestyle: How Do Frogs and Toads Behave?
Behaviorally, frogs and toads also exhibit unique traits. Frogs are more active and agile, often leaping great distances to escape predators or catch prey. Toads, in contrast, are less agile and prefer to walk or make short hops. They rely more on camouflage and toxin secretion for defense.
Frogs are generally more vocal than toads, producing a wide range of calls to attract mates or ward off competitors. Toads, while also vocal, have a more limited repertoire of sounds. The difference in their calls is often a result of their habitats and mating strategies.
Reproduction and Lifecycle: How Do Frogs and Toads Reproduce?
Both frogs and toads lay eggs, but their reproductive strategies differ significantly. Frogs lay their eggs in clusters, often in water, where they hatch into free-swimming tadpoles. Toads, on the other hand, lay their eggs in long strings, which are typically wrapped around aquatic plants.
The metamorphosis process is similar for both, involving a transformation from tadpole to adult. However, toads' tadpoles are usually hardier and can survive in less ideal conditions compared to frog tadpoles.
Dietary Habits: What Do Frogs and Toads Eat?
Frogs and toads are both carnivorous, feeding primarily on insects, worms, and other small invertebrates. Frogs are more likely to hunt actively, using their long, sticky tongues to catch prey. Toads, being less active, often rely on ambush tactics, waiting patiently for prey to come within range.
Their diets play a crucial role in controlling insect populations, making them valuable allies in ecosystems and agriculture.
Predators and Defense: How Do Frogs and Toads Protect Themselves?
Both frogs and toads have developed various defense mechanisms to survive predation. Frogs rely on their agility and ability to leap into water to escape predators. Their bright colors can also warn predators of their toxicity.
Toads, on the other hand, use their rough, camouflaged skin to blend into their surroundings. Their parotoid glands secrete toxins that can irritate or harm predators, providing an additional layer of defense.
Frog vs Toad Evolution: How Are They Related?
Frogs and toads share a common evolutionary ancestor and belong to the order Anura. Over millions of years, they have diverged into different families, adapting to various habitats and ecological niches. Understanding their evolutionary history provides insights into their unique adaptations and survival strategies.
Ecological Role: Why Are Frogs and Toads Important?
Both frogs and toads play vital roles in ecosystems. They act as both predators and prey, maintaining a balance in the food chain. Their sensitivity to environmental changes makes them important bioindicators, helping scientists monitor ecosystem health.
Common Myths: Are Frogs and Toads Really That Different?
Despite their differences, frogs and toads are often misunderstood. Common myths include the idea that toads cause warts (they don’t) or that all frogs are poisonous (only a few species are). Debunking these myths helps us better appreciate these incredible creatures.
Can You Tell Them Apart at a Glance?
While it can be challenging, knowing the key differences in physical traits, habitat preferences, and behavior can help you distinguish between frogs and toads with ease.
Frog vs Toad in Popular Culture
Frogs and toads have made their mark in folklore, literature, and popular culture. From fairy tales like "The Frog Prince" to modern memes, these amphibians have captured human imagination for centuries.
How to Care for Frogs and Toads as Pets?
Caring for frogs and toads requires understanding their specific needs, including habitat setup, diet, and temperature control. While they can make fascinating pets, their care demands commitment and knowledge.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Are frogs and toads the same species? No, frogs and toads are different species within the order Anura.
- Can toads live in water? While toads can survive near water, they are more terrestrial than frogs.
- Do all frogs have smooth skin? Most frogs have smooth skin, but some species have a rough texture.
- Are all toads poisonous? Not all toads are poisonous, but many secrete toxins as a defense mechanism.
- Can you keep frogs and toads together as pets? It’s not recommended, as their needs and behaviors can differ significantly.
- What is the lifespan of frogs and toads? Frogs and toads can live anywhere from a few years to over a decade, depending on the species.
Conclusion
In the debate of frog vs toad, both creatures bring unique qualities to the table. From their physical traits to their ecological roles, frogs and toads are remarkable examples of nature’s diversity. By understanding their differences and appreciating their similarities, we can foster a deeper respect for these amphibians and the ecosystems they inhabit.
Article Recommendations