When it comes to amphibians, few creatures capture our curiosity like the toad and the frog. These two species, often mistaken for one another, boast unique characteristics that set them apart in the animal kingdom. From their physical traits to their habitats and behaviors, the differences between toads and frogs are as fascinating as they are diverse. But what exactly distinguishes these two amphibians? And why are their roles in the ecosystem so critical?
In this definitive guide, we’ll delve into the intriguing world of toads and frogs, unpacking their distinct features, habitats, and ecological importance. Whether you're a nature enthusiast, a biology student, or simply someone who’s spotted a hopping creature in your garden and wondered whether it’s a toad or a frog, this article will leave no stone unturned. With well-researched insights, we’ll help you understand the unique traits that make these amphibians both similar and different.
So, let’s leap right in! From their physical differences to their diets, lifecycles, and even their symbolic significance in various cultures, this article will serve as your ultimate resource on toad vs frog. Stay tuned, as we’ll even bust common myths and answer frequently asked questions to clear up any confusion between these two fascinating creatures.
Read also:Toprated Best Home Warranty Companies To Protect Your Home
Table of Contents
- What are the physical differences between toads and frogs?
- Where do toads and frogs live?
- Why do toads have rough skin while frogs are smooth?
- What do toads and frogs eat?
- How do toads and frogs behave differently?
- How do toads and frogs reproduce?
- What are the differences in their lifespan and growth?
- What roles do toads and frogs play in the ecosystem?
- What is the cultural significance of toads and frogs?
- What are the common myths about toads and frogs?
- Scientific classifications of toads and frogs
- Toad vs Frog: How are they represented in popular media?
- What is their conservation status?
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Conclusion
What are the physical differences between toads and frogs?
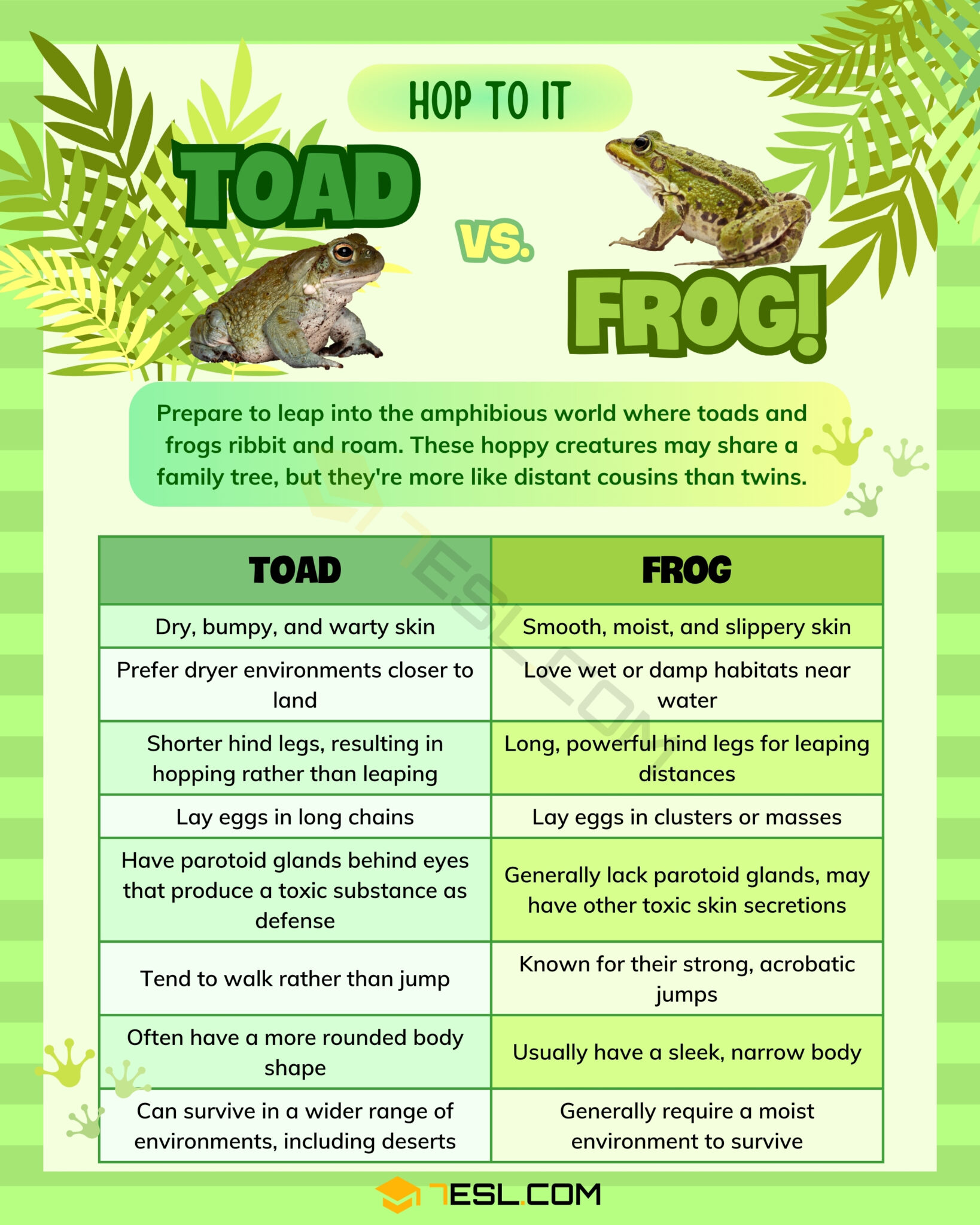
One of the most noticeable distinctions between toads and frogs lies in their physical appearance. Frogs generally have smooth, moist skin, which allows them to thrive in aquatic or semi-aquatic environments. On the other hand, toads are known for their dry, warty skin, which helps them adapt to drier habitats.
In terms of body shape, frogs tend to have a slender, athletic build with long, powerful hind legs designed for jumping. Toads, however, are more robust and squat, with shorter legs that make them better suited for crawling rather than leaping long distances.
Additionally, frogs usually have bulging eyes that give them excellent peripheral vision, crucial for spotting predators or prey. Toads, by contrast, have more recessed eyes, and their pupils are often horizontal rather than round.
Where do toads and frogs live?
The habitats of toads and frogs differ significantly, although both are amphibians. Frogs are typically found near water sources such as ponds, lakes, and streams. Their permeable skin requires them to stay in moist environments to prevent dehydration.
Toads, however, are more terrestrial and can be found in a variety of environments, including forests, grasslands, and even gardens. Their tough, dry skin enables them to survive in less humid conditions, making them more adaptable to drier climates.
Why do toads have rough skin while frogs are smooth?
The texture of their skin is a key adaptation to their respective environments. Frogs rely on their smooth, slimy skin for moisture and respiration, as they absorb oxygen directly through their skin. The mucus coating also helps ward off predators by making them slippery and difficult to grasp.
Read also:Where Does Translation Take Place In The Intricate World Of Biology
Toads, on the other hand, have rough, warty skin that serves as camouflage and protection. The bumps on their skin are often mistaken for warts but are actually glands that secrete toxins to deter predators.
What do toads and frogs eat?
Both toads and frogs are carnivorous and primarily feed on insects, making them valuable pest controllers in ecosystems. Frogs are known for their sticky, extendable tongues, which they use to catch flies, mosquitoes, and other small insects.
Toads have a similar diet but may also consume larger prey, such as beetles and earthworms. Unlike frogs, toads are more opportunistic feeders and can eat a wide variety of invertebrates they come across.
How do toads and frogs behave differently?
Behavioral patterns in toads and frogs are shaped by their environments and physical traits. Frogs are more active and agile, often leaping long distances to escape predators. Their vocalizations are also more varied and are often heard near water bodies during mating seasons.
Toads are more sedentary and rely on camouflage and toxins for protection. They are less vocal than frogs and are more likely to hop short distances or crawl when threatened.
How do toads and frogs reproduce?
Both toads and frogs reproduce by laying eggs, but the appearance and location of their eggs differ. Frogs lay their eggs in clusters or masses, usually in water. These eggs hatch into tadpoles, which eventually metamorphose into adult frogs.
Toads, on the other hand, lay their eggs in long chains, often in shallow water. Like frogs, their eggs hatch into tadpoles, but the transformation process may take longer depending on environmental conditions.
What are the differences in their lifespan and growth?
Frogs generally have a shorter lifespan compared to toads, averaging around 10–12 years in the wild. Toads can live up to 15 years or more, especially in captivity.
The growth and development of both species are influenced by factors such as climate, food availability, and predation pressure. Frogs grow rapidly during the larval stage to adapt to their aquatic environment, while toads develop more slowly, allowing them to thrive in less aquatic settings.
What roles do toads and frogs play in the ecosystem?
Toads and frogs are vital components of their ecosystems. As predators, they help control insect populations, reducing the spread of diseases such as malaria and dengue. They also serve as prey for a wide range of animals, including birds, snakes, and mammals.
In addition, their presence in an ecosystem is a strong indicator of environmental health. Amphibians are highly sensitive to pollution and climate change, making them crucial bioindicators for scientists studying ecological balance.
What is the cultural significance of toads and frogs?
Toads and frogs have been featured in myths, folklore, and literature across cultures. Frogs are often associated with transformation and renewal, as seen in fairy tales like "The Frog Prince." Toads, on the other hand, are sometimes linked to witchcraft and superstition, but they are also symbols of protection and fertility in certain cultures.
What are the common myths about toads and frogs?
Several myths surround toads and frogs, many of which are rooted in misunderstanding. For example, many people believe that touching a toad can cause warts. This is entirely false, as warts in humans are caused by a virus, not by contact with amphibians.
Another common myth is that all frogs are poisonous. While some species produce toxins, the majority are harmless to humans.
Scientific classifications of toads and frogs
Frogs and toads both belong to the order Anura, which means "without a tail." However, they are classified into different families. Frogs are typically part of the Ranidae family, while toads belong to the Bufonidae family.
These classifications are based on physical traits, behaviors, and genetic differences, further highlighting the distinctions between these two amphibian groups.
Toad vs Frog: How are they represented in popular media?
From children's books to animated films, toads and frogs have captured imaginations worldwide. Frogs are often portrayed as friendly, whimsical characters, such as Kermit the Frog from "The Muppets." Toads, on the other hand, are sometimes depicted as grumpier or more mysterious figures, like Mr. Toad from "The Wind in the Willows."
What is their conservation status?
Many species of toads and frogs are under threat due to habitat loss, climate change, and pollution. Conservation efforts, such as habitat restoration and breeding programs, are critical to preserving these amphibians.
Organizations like Amphibian Ark and the IUCN are actively working to protect endangered species and ensure their survival for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can a toad turn into a frog?
No, a toad cannot turn into a frog. They are distinct species with different physical and behavioral traits.
2. Are toads poisonous?
Some toads secrete toxins from their skin to deter predators, but not all toads are poisonous to humans.
3. Do frogs and toads live together?
While frogs and toads can share the same habitat, they have different preferences for living conditions and do not typically interact.
4. How can you tell a frog from a toad?
Frogs have smooth, moist skin and long legs, while toads have dry, warty skin and shorter legs.
5. Do frogs and toads make the same sounds?
No, frogs are generally more vocal with a wide range of calls, while toads are less vocal and produce deeper croaks.
6. Are toads and frogs endangered?
Some species of toads and frogs are endangered due to environmental threats, but others are thriving in their natural habitats.
Conclusion
Toads and frogs are remarkable creatures that play essential roles in ecosystems around the world. Despite their similarities, their differences in appearance, behavior, and habitat make them unique in their own right. By understanding these distinctions, we can better appreciate the diversity of life and the importance of conservation efforts to protect these amphibians for generations to come.
Whether you encounter a warty toad in your garden or a sleek frog by a pond, remember that both contribute significantly to the balance of nature. Let’s do our part to ensure their survival and celebrate the wonderful diversity they bring to our planet!
Article Recommendations