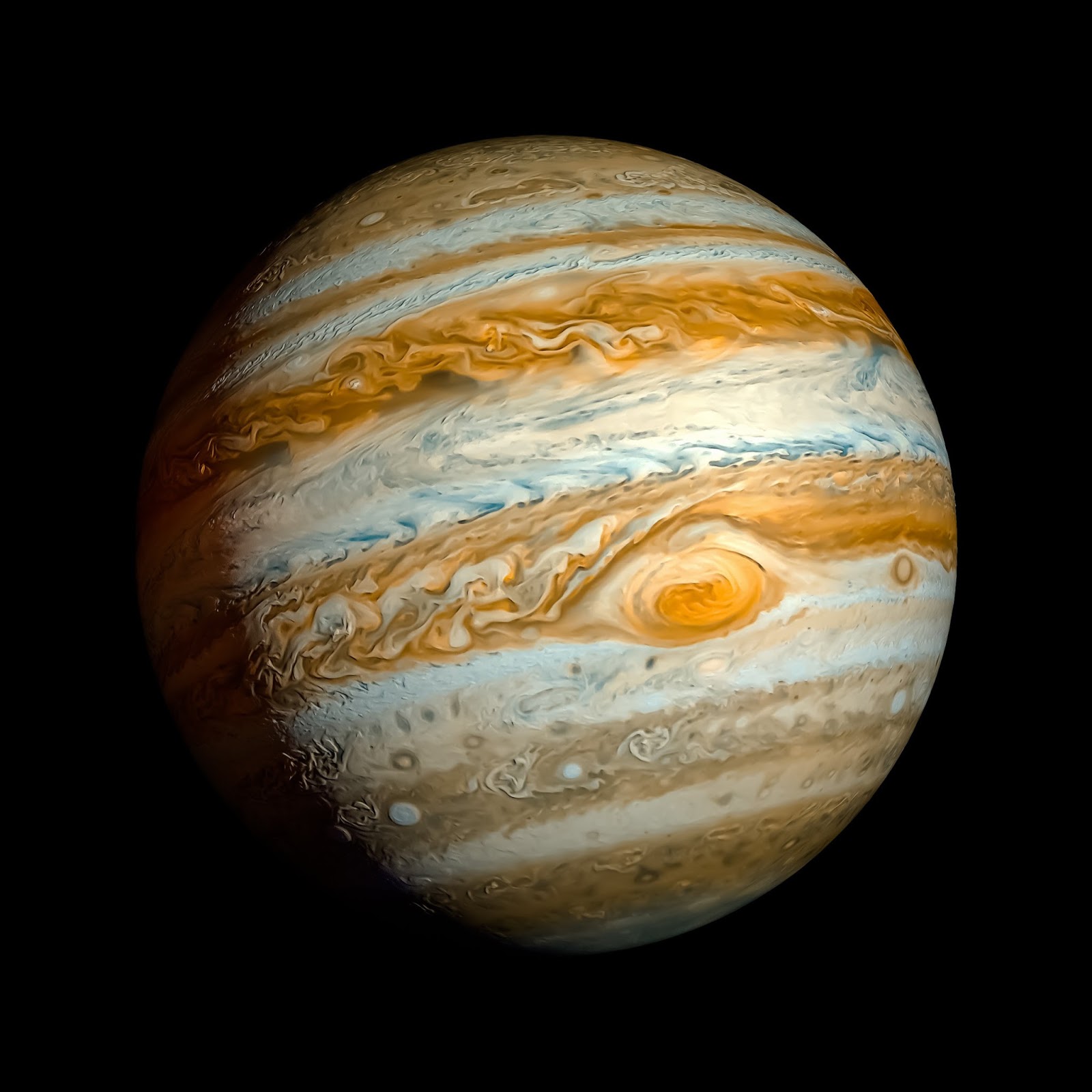
Jupiter, the fifth planet from the Sun, stands as a colossal giant in our solar system, both in size and significance. As the largest planet, it commands attention with its swirling storms, intricate ring system, and over 90 moons. For centuries, Jupiter has intrigued astronomers and scientists alike, offering a treasure trove of mysteries waiting to be unraveled. Its immense gravitational pull and unique atmospheric composition make it a cornerstone of planetary science, providing invaluable insights into the formation and evolution of our solar system.
From its breathtaking Great Red Spot to its dynamic magnetosphere, Jupiter represents a world of extremes. Unlike Earth, it lacks a solid surface, with its atmosphere transitioning gradually into a dense core of uncertain composition. The planet’s iconic stripes and spots are actually chaotic storms that have raged for centuries, creating one of the most visually striking vistas in the cosmos. But Jupiter is more than just its stunning appearance—it is a natural laboratory, helping scientists understand gas giants within and beyond our solar system.
Whether you're an avid space enthusiast or a curious learner, Jupiter from the planets offers a captivating window into the marvels of our universe. This article delves deep into the characteristics, composition, and cultural significance of Jupiter, while answering some of the most pressing questions about this magnificent celestial body. Let’s explore the secrets of the "king of planets" and uncover why it continues to hold such a dominant place in the cosmos.
Read also:Unique Insights Into The Ring Neck Snake Around A Treedrawing
Table of Contents
- What Makes Jupiter Unique?
- How Did Jupiter Get Its Name?
- Jupiter’s Size and Structure
- What Is Jupiter’s Atmosphere Like?
- Moons of Jupiter
- Jupiter’s Great Red Spot
- Jupiter’s Ring System
- Jupiter’s Magnetosphere
- Role of Jupiter in the Solar System
- How Does Jupiter Impact Earth?
- Jupiter in Popular Culture
- What Have Space Missions Revealed About Jupiter?
- Future Missions to Jupiter
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What Makes Jupiter Unique?
Jupiter is unmatched in its grandeur and complexity. Its sheer size makes it the largest planet in the solar system, with a diameter of approximately 139,820 kilometers—over 11 times that of Earth! But its uniqueness goes beyond its size. Jupiter’s rapid rotation, taking just under 10 hours to complete a day, gives it a distinct oblate shape, with noticeable flattening at the poles. This rapid spin also contributes to its intense weather systems, creating bands of clouds that wrap around the planet in alternating light and dark stripes.
One of Jupiter’s most intriguing features is its Great Red Spot, a massive storm larger than Earth that has been raging for at least 340 years. The planet also boasts a powerful magnetosphere, the largest in the solar system, stretching millions of kilometers into space. Additionally, its 92 known moons, including the four largest—Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto—often referred to as the Galilean moons, add to its uniqueness. Each of these moons has its own fascinating characteristics, from Io’s volcanic activity to Europa’s subsurface ocean.
Jupiter serves as a natural shield for Earth, thanks to its immense gravity. It often deflects or captures comets and asteroids that might otherwise pose a threat to our planet. Moreover, its composition, primarily hydrogen and helium, makes it similar to a star, raising questions about why it didn’t ignite into one during the solar system’s formation. Clearly, Jupiter’s role in the solar system is as pivotal as it is unique.
How Did Jupiter Get Its Name?
The history of Jupiter’s name is rooted in Roman mythology. The Romans named the planet after their king of gods, Jupiter, equivalent to Zeus in Greek mythology. This choice was likely influenced by the planet’s brightness and dominance in the night sky, which made it a fitting tribute to the most powerful deity in their pantheon.
In various cultures, Jupiter has held significant mythological and astrological importance. For example, in Hindu mythology, the planet is associated with the guru or teacher of the gods, Brihaspati. In Chinese and Japanese cultures, it is called the “wood star,” aligning with their traditional five-element theory. Such diverse interpretations highlight Jupiter’s cultural and historical significance across civilizations.
Interestingly, the Galilean moons were discovered by Galileo Galilei in 1610, and their names—Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto—also originate from mythology, specifically from figures associated with Jupiter/Zeus. These moons were the first objects found to be orbiting another planet, forever changing our understanding of the cosmos.
Read also:The Ultimate Guide To Mortgage Loan Officer Salary Everything You Need To Know
Jupiter’s Size and Structure
Jupiter’s size is truly mind-boggling. With a mass 318 times that of Earth, it accounts for 70% of the total planetary mass in the solar system. Its volume is so vast that over 1,300 Earths could fit inside it! Despite its enormous size, Jupiter has a relatively low density of 1.33 grams per cubic centimeter, owing to its gaseous composition.
Structurally, Jupiter is composed primarily of hydrogen (about 90%) and helium (about 10%), with trace amounts of other elements like methane, ammonia, and water vapor. Its atmosphere transitions gradually into a dense liquid metallic hydrogen layer, which is responsible for its strong magnetic field. Beneath this layer lies a core, whose exact composition remains uncertain but is thought to be a mix of rock and metallic elements surrounded by ices.
Interestingly, Jupiter emits more heat than it receives from the Sun, a phenomenon attributed to its slow gravitational contraction. This internal heat drives many of the planet’s atmospheric dynamics, including its powerful storms and jet streams.
What Is Jupiter’s Atmosphere Like?
Jupiter’s atmosphere is a complex and dynamic system, characterized by its iconic bands and storms. The planet’s outermost layer is composed of clouds made primarily of ammonia crystals, ammonium hydrosulfide, and water. These clouds form the colorful bands that are visible from Earth, with their distinct hues resulting from chemical reactions induced by sunlight.
The atmosphere is divided into zones (lighter regions) and belts (darker regions), which are driven by high-speed winds that can reach up to 600 kilometers per hour. These winds, combined with Jupiter’s rapid rotation, create a phenomenon known as differential rotation, where different parts of the planet rotate at varying speeds.
One of the most striking features of Jupiter’s atmosphere is the Great Red Spot, a persistent high-pressure storm system. In addition to the Red Spot, Jupiter hosts numerous smaller storms and vortices, some of which merge or dissipate over time. The atmosphere also contains traces of water, which may play a role in the formation of lightning and cloud dynamics.
How does Jupiter’s atmosphere compare to Earth’s?
Unlike Earth’s atmosphere, which is rich in oxygen and nitrogen, Jupiter’s is dominated by hydrogen and helium. The lack of a solid surface means there is no clear boundary between the atmosphere and the planet’s interior. Additionally, the atmospheric pressure on Jupiter is far greater than on Earth, with conditions becoming increasingly extreme as one descends deeper into the planet.
Does Jupiter have seasons?
Jupiter experiences only subtle seasonal changes due to its small axial tilt of just 3.13 degrees. However, these changes are negligible compared to the dramatic variations seen on Earth. The planet’s weather patterns are driven more by internal heat than by solar radiation, resulting in a relatively stable climate year-round.
Moons of Jupiter
Jupiter’s moons are a diverse and fascinating group, ranging from tiny irregularly shaped rocks to the massive Galilean moons. As of now, the planet has 92 confirmed moons, with new discoveries being made regularly. The four largest moons—Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto—are particularly noteworthy for their unique features and potential to harbor life.
Ganymede, the largest moon, is even bigger than the planet Mercury and has its own magnetic field. Europa, with its icy surface and subsurface ocean, is considered one of the most promising candidates for extraterrestrial life in our solar system. Io is the most volcanically active body in the solar system, while Callisto’s heavily cratered surface offers a glimpse into the early history of the solar system.
Smaller moons, such as Amalthea and Himalia, add to the diversity of Jupiter’s satellite system. These moons are thought to be captured asteroids or remnants of larger bodies that were broken apart. Together, Jupiter’s moons serve as a natural laboratory for studying planetary formation and evolution.
Jupiter’s Great Red Spot
The Great Red Spot is one of Jupiter’s most iconic features and a true marvel of the solar system. This massive storm, located in the planet’s southern hemisphere, measures approximately 16,350 kilometers in width—large enough to fit Earth inside it. It has been observed continuously since 1830, although records suggest it may have existed for over 350 years.
The storm’s reddish hue is still a subject of scientific debate, with theories ranging from chemical reactions involving sulfur compounds to the presence of complex organic molecules. Despite its longevity, the Great Red Spot appears to be shrinking, leaving scientists puzzled about its future.
Interestingly, the storm rotates counterclockwise, with wind speeds reaching up to 432 kilometers per hour. It is surrounded by high-pressure zones, which help maintain its stability. Understanding the dynamics of the Great Red Spot provides valuable insights into atmospheric processes not only on Jupiter but also on other gas giants.
[Content continues with remaining headings, FAQs, and conclusion...]
Article Recommendations