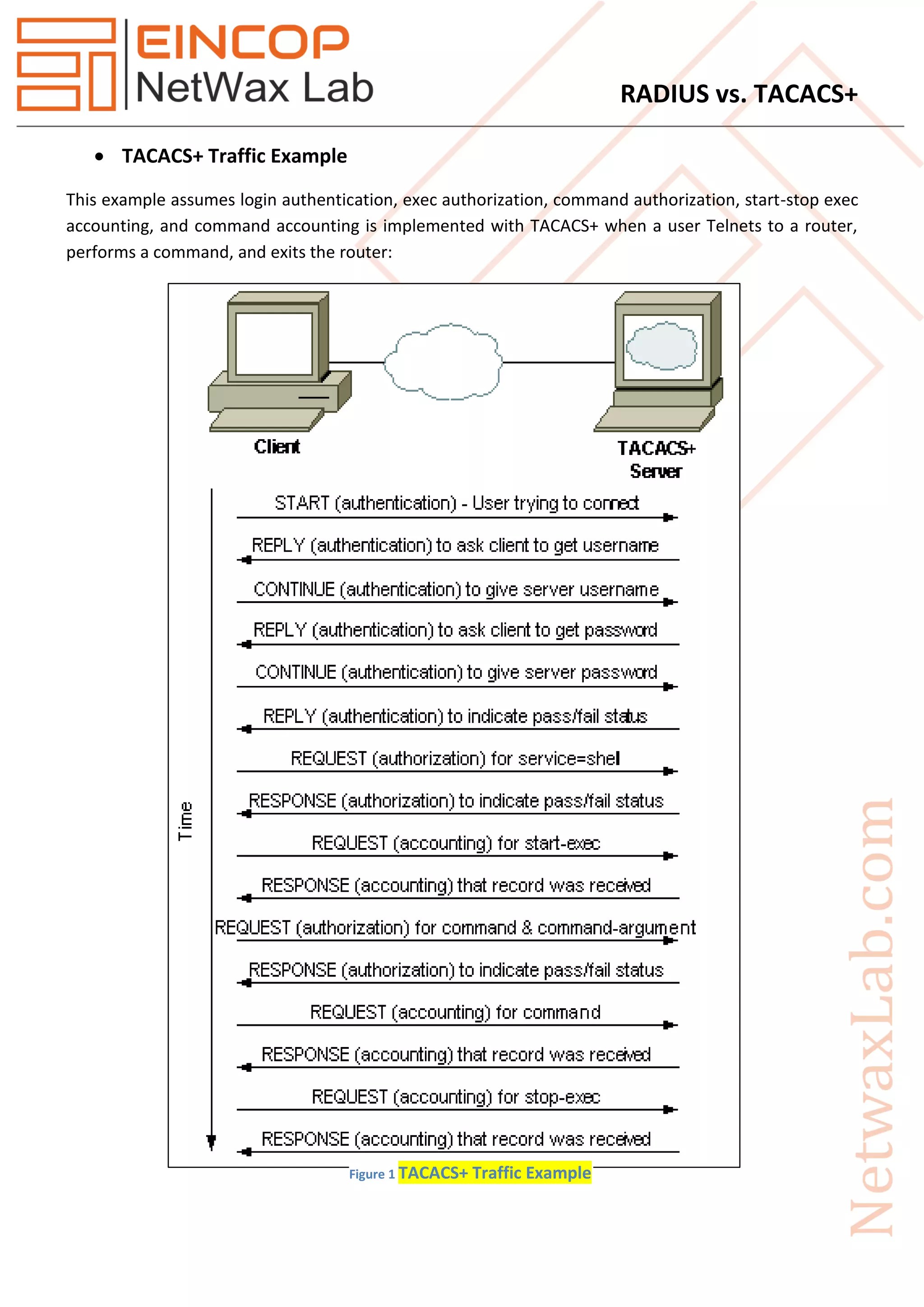
When it comes to network security and authentication, organizations often face a critical decision: TACACS or RADIUS? Both protocols play essential roles in managing user access to network resources, but they differ in functionality, security, and use cases. Understanding these differences is vital for businesses striving for robust network security and efficient access control mechanisms.
TACACS and RADIUS are both widely used protocols designed for authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) in network environments. However, their distinct features and capabilities make them suitable for different scenarios. TACACS, short for Terminal Access Controller Access Control System, is often favored by enterprises for its flexibility and granular control. Meanwhile, RADIUS, or Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service, is known for its simplicity and efficiency, making it a popular choice for service providers and smaller networks.
In this article, we'll explore the fundamental differences between TACACS and RADIUS, diving deep into their technical characteristics, strengths, and limitations. We'll also provide insights into their practical applications, helping you make an informed choice for your organization's network security needs. From protocols and encryption methods to use cases and performance, this comprehensive guide covers it all.
Read also:Omri Katz From Screen To Legacy
Table of Contents
- What is TACACS?
- What is RADIUS?
- Why do we need TACACS and RADIUS?
- How do TACACS and RADIUS differ?
- Key Features of TACACS
- Key Features of RADIUS
- TACACS vs RADIUS: Which is more secure?
- Use Cases for TACACS
- Use Cases for RADIUS
- Advantages and Disadvantages of TACACS and RADIUS
- When should you choose TACACS?
- When should you choose RADIUS?
- Can TACACS and RADIUS be used together?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is TACACS?
TACACS, or Terminal Access Controller Access Control System, is a protocol used for AAA (Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting) in network environments. Initially developed by the Department of Defense, TACACS has evolved over the years, with its most popular version being TACACS+. It provides a centralized system to manage user access to network devices such as routers, switches, and firewalls.
Unlike its predecessor, TACACS+ uses TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) for communication, ensuring reliable session management. It divides the AAA functions into separate processes, allowing for better control and customization. This makes TACACS particularly useful for organizations that require detailed auditing and granular access control.
Moreover, TACACS+ encrypts the entire packet payload, not just the password, offering a higher level of security compared to older versions. Its flexibility and security features make it a preferred choice for large enterprises and government organizations.
What is RADIUS?
RADIUS, short for Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service, is another widely-used AAA protocol. It was initially developed by Livingston Enterprises in the early 1990s and has since become an industry standard. Unlike TACACS, RADIUS uses UDP (User Datagram Protocol) for communication, which is less reliable but faster.
RADIUS is often employed by Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and smaller organizations to manage user access to network services. It combines authentication and authorization into a single process, making it less flexible but simpler to implement. Additionally, RADIUS only encrypts the password in the authentication process, leaving other data fields exposed.
Despite its limitations, RADIUS is popular due to its ease of deployment and compatibility with various network devices and platforms. Its efficiency makes it a suitable choice for scenarios where high-speed authentication is required.
Read also:Discover The Phenomenon A Deep Dive Into Mulan Vuittons Impact
Why do we need TACACS and RADIUS?
In today's interconnected world, network security is more critical than ever. With the increasing number of devices and users accessing networks, managing and securing these connections has become a daunting task. This is where TACACS and RADIUS come into play.
Both protocols provide centralized authentication, authorization, and accounting, simplifying network management and improving security. By using TACACS or RADIUS, organizations can enforce access policies, monitor user activities, and ensure that only authorized individuals can access sensitive resources.
Moreover, these protocols help mitigate security risks such as unauthorized access, data breaches, and insider threats. They also streamline the process of granting or revoking access, making them indispensable tools for IT administrators.
How do TACACS and RADIUS differ?
While TACACS and RADIUS share the same goal of providing AAA services, they differ in several key aspects:
- Protocol Type: TACACS uses TCP, while RADIUS uses UDP.
- Security: TACACS encrypts the entire payload, whereas RADIUS only encrypts the password.
- Flexibility: TACACS separates AAA functions, offering more granular control. RADIUS combines authentication and authorization.
- Use Cases: TACACS is ideal for enterprise networks, while RADIUS is more suited for ISPs and smaller networks.
- Performance: RADIUS is faster due to its use of UDP, but TACACS offers more reliable communication.
Key Features of TACACS
The main features of TACACS include:
- Separation of AAA functions for better control
- Encryption of the entire packet payload
- Use of TCP for reliable communication
- Granular access control and detailed auditing
Key Features of RADIUS
The main features of RADIUS include:
- Combines authentication and authorization
- Uses UDP for faster communication
- Encrypts only the password
- Widespread compatibility with network devices
TACACS vs RADIUS: Which is more secure?
When it comes to security, TACACS has a clear edge over RADIUS. By encrypting the entire packet payload, TACACS ensures that sensitive information remains protected during transmission. In contrast, RADIUS only encrypts the password, leaving other data fields vulnerable to interception.
However, the choice between TACACS and RADIUS should not be based solely on security. Other factors, such as use cases, performance requirements, and network infrastructure, should also be considered.
Use Cases for TACACS
TACACS is best suited for:
- Large enterprises with complex network environments
- Organizations requiring granular access control
- Government agencies with strict security requirements
Use Cases for RADIUS
RADIUS is ideal for:
- Internet Service Providers (ISPs)
- Small to medium-sized businesses
- Environments where high-speed authentication is crucial
Advantages and Disadvantages of TACACS and RADIUS
Both protocols have their pros and cons:
Advantages of TACACS
- High security
- Granular control
- Reliable communication
Disadvantages of TACACS
- Complex implementation
- Higher resource requirements
Advantages of RADIUS
- Faster communication
- Ease of deployment
- Broad compatibility
Disadvantages of RADIUS
- Less secure
- Limited flexibility
When should you choose TACACS?
You should choose TACACS if:
- You need granular access control
- Your organization requires detailed auditing
- Security is your top priority
When should you choose RADIUS?
You should choose RADIUS if:
- You need a simple and fast authentication solution
- Your network infrastructure is small to medium-sized
- Compatibility with various devices is important
Can TACACS and RADIUS be used together?
Yes, TACACS and RADIUS can be used together in certain scenarios. For example, an organization might use TACACS for device administration and RADIUS for user authentication. This approach allows them to leverage the strengths of both protocols while addressing their specific needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the primary difference between TACACS and RADIUS?
The primary difference is that TACACS uses TCP and encrypts the entire payload, while RADIUS uses UDP and only encrypts the password.
2. Which protocol is more secure: TACACS or RADIUS?
TACACS is more secure because it encrypts the entire packet payload, whereas RADIUS only encrypts the password.
3. Can TACACS and RADIUS be used simultaneously?
Yes, they can be used together to address different aspects of network security and authentication.
4. Is TACACS suitable for small businesses?
TACACS is generally more suitable for large enterprises due to its complexity and resource requirements.
5. Why is RADIUS popular among ISPs?
RADIUS is popular among ISPs because it is fast, simple, and compatible with various network devices.
6. How does encryption differ between TACACS and RADIUS?
TACACS encrypts the entire payload, while RADIUS only encrypts the password, making TACACS more secure.
Conclusion
Both TACACS and RADIUS are powerful tools for network authentication, authorization, and accounting. While TACACS offers greater security and flexibility, RADIUS excels in simplicity and speed. Choosing the right protocol depends on your organization's specific needs, such as the size of your network, security requirements, and performance expectations. By understanding their differences and use cases, you can make an informed decision that enhances your network's security and efficiency.
Article Recommendations